- Notes
- Exam
- Nursing Care Plan
Notes
Exam
Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Diagnosis
Ineffective Breathing Pattern related to neuromuscular weakness of the respiratory muscles and throat.
Desired outcomes
The patient will maintain an oxygen saturation of >92% and a respiratory rate of 12-20 with ADL’s.
Nursing Interventions
- Assess for signs of activity intolerance. Ask client to rate perceived exertion.
- Rationale: Dyspnea on exertion, palpitations, headaches, or dizziness or patient states increased exertion level, are all signs of activity intolerance and decreased tissue oxygenation.
- Monitor pulse oximetry and report O2 saturation <92%.
- Rationale: O2 sat of <92% indicates the need to supplement oxygen.
- Monitor the patients pulse oximetry every 4-6 hours.
- Rationale: An O2 saturation of less than 92% may detect hypoxia and signals the need for supplemental oxygen.
- Encourage deep breathing exercises and administer oxygen if indicated
- Rationale: Increases oxygen delivery to the body.
Nursing Diagnosis
Risk for Aspiration related to difficulty swallowing
Desired outcomes
Client is able to swallow independently without choking. Able to maintain a patent airway.
Nursing Interventions
- Assess for signs of activity intolerance. Ask client to rate perceived exertion.
- Rationale: Dyspnea on exertion, palpitations, headaches, or dizziness or patient states increased exertion level, are all signs of activity intolerance and decreased tissue oxygenation.
- Monitor pulse oximetry and report O2 saturation <92%.
- Rationale: O2 sat of <92% indicates the need to supplement oxygen.
Nursing Diagnosis
Self-Care Deficit related to muscle weakness, general fatigue.
Desired outcomes
Patient is able to perform self-care activities independently and able to demonstrates ability to use adaptive devices for completion on ADL’s.
Nursing Interventions
- Observe the patient’s ability to perform activities of daily living.
- Rationale: This will show performance challenges and the level which the patient needs assistance with completing ADL’s.
- Allow enough time for task performance. DO not rush patient. Involve family and significant others in care activities. Observe activities to ensure patient can perform them safely without assistance.
- Rationale: Allowing sufficient time preserves the patients energy and increases activity tolerance.
Nursing Diagnosis
Activity intolerance related to muscle weakness
Characterized by:
Subjective Data:
- Patients say tired after doing the activity.
- Patients report muscle weakness.
Objective Data:
- Patient seems tired and listless.
- Patient was not able to take action to meet their daily needs.
- Increased pulse.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Breathing increases.
- Decreased muscle strength.
Outcomes
- Full muscle strength.
- Atrophy does not occur.
- Good muscle tone.
- Patients can perform the activity gradually.
- Muscle weakness does not occur.
Nursing Interventions
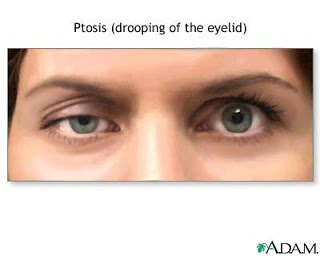
- Assess the strength of muscles, ptosis, diplopia, eye movement, ability to chew, swallow, cough reflex, talk.
- Rationale: The rate of muscle weakness may be different in other parts of the body.
- Assess muscle strength before and after drug administration.
- Rationale: Knowing the effects of drug administration.
- Perform scheduled breaks, keep quiet surroundings.
- Rationale: Period after the break, increased muscle strength.
- Encourage participation in treatment.
- Rationale: Train activity gradually.
Nursing Diagnosis
Impaired verbal communication related to muscle weakness.
Characterized by:
Subjective Data:
- Patients say difficulty speaking
Data Objective :
- Patients appear to difficulties in verbal expression.
- Changes in behavior are not willing to communicate.
- The use of sign language / body.
Outcomes
Patients expressing themselves verbally or non-verbally.
Nursing Interventions
- Assess the patient’s ability to speak with the examination of cranial nerves V, VII, IX, X, XII.
- Rationale: knowing the patient’s ability to speak.
- Ask a closed question, yes or no or body movements.
- Rationale: Facilitate patient easily answered.
- Talk with slow motion.
- Rationale: Can see the speaker’s lip movements.
- Use images, paper or other means.
- Rationale: Using media allows patients to express desire.
- Inform staff or family, about the limitations of the patient in communication.
- Rationale: Communication patterns that one would add to the frustration of patients.